Simple Temperature Control by using Fuzzy Logic Control Based on Arduino [LEP]

ในตอนสุดท้ายของการควบคุมอุณหภูมิแบบฟัซซี่ลอจิก (Fuzzy Logic Control : FLC) โดยใช้บอร์ด Arduino UNO ครั้งนี้ จะเป็นอีกตัวอย่างหนึ่งของการควบคุมอุณหภูมิด้วยการกำหนดค่า Setpoint ที่ชัดเจนเช่น ต้องการอุณหภูมิที่ 20°C หรือ 25°C และนำค่า Error และ DeltaError เป็นสัญญาณอินพุตฟัซซี่ลอจิก (อินพุต 2 ส่วน) สำหรับควบคุมการทำงานของระบบและใช้ไลบารี่ฟัซซี่ลอจิก <Fuzzy.h> ในการเขียนโปรแกรม สำหรับสัญญาณเอาต์พุตจะใช้เพียง 1 ช่องในลักษณะของพัลซ์วิดธ์มอดูเลตชั่นเพื่อให้เห็นผลที่เกิดขึ้น หรือจะนำไปใช้ในการควบคุมพัดลมหรือคอมเพลสเซอร์ได้ตามต้องการ
Download Arduino Library Fuzzy logic Control
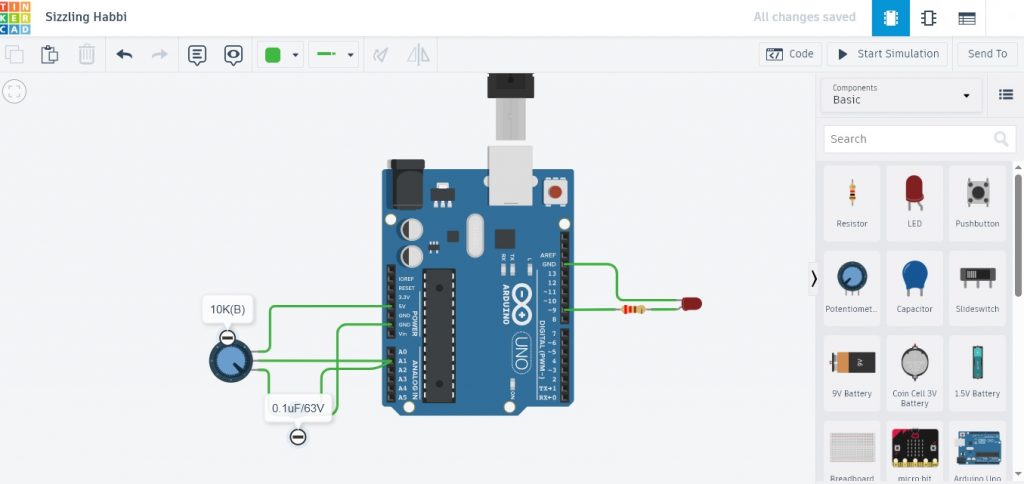
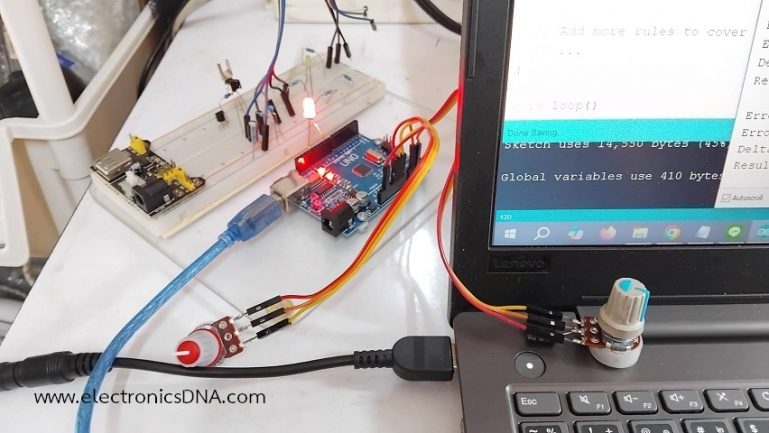
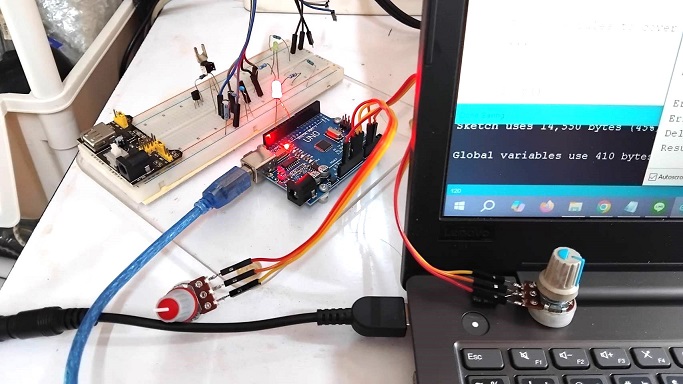
ในรูปที่ 1 และรูปที่ 2 แสดงลักษณะการต่ออุปกรณ์สำหรับทดลองและวงจรที่ใช้ในการทดลองการควบคุมแบบฟัซซี่ลอจิก โดยในการทดลองครั้งนี้จะใช้ตัวต้านทานปรับค่า (Variable Resistor : VR) เพื่อทดสอบการทำงานแทนค่าเซนเซอร์อุณหภูมิที่อ่านได้ในส่วนของอินพุตฟัซซี่ลอจิก ในส่วนเอาต์พุตจะส่งเป็นสัญญาณพัลซ์วิดธ์มอดูเลตชั่นที่ขา D9 และต่อแอลอีดีเพื่อสังเกตผลที่ได้จากการทำงาน
// Arduino_advanced_sample_V6
#include <Fuzzy.h>
int setpoint = 20; // (20°C)
int Error = 0;
int DeltaError = 0;
int previousError = 0;
int PWMoutput = 0; // PWM value (0-255)
Fuzzy *fuzzy = new Fuzzy(); // Fuzzy
// FuzzyInput1
FuzzySet *error_NB = new FuzzySet(-40, -40, -20, -5);
FuzzySet *error_Z = new FuzzySet(-10, 0, 0, 10);
FuzzySet *error_PS = new FuzzySet(5, 20, 40, 40);
// FuzzyInput2
FuzzySet *deltaError_NS = new FuzzySet(-40, -30, -20,-5);
FuzzySet *deltaError_Z = new FuzzySet(-10, 0, 0, 10);
FuzzySet *deltaError_PS = new FuzzySet(5, 20, 40, 40);
// FuzzyOutput
FuzzySet *slowOutput = new FuzzySet(-5, -5, -2, -2);
FuzzySet *normalOutput = new FuzzySet(-1, 0, 0, 1);
FuzzySet *quickOutput = new FuzzySet(2, 2, 5, 5);
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600); // Set the Serial output
pinMode(9,OUTPUT); // PWM Pin
// Every setup must occur in the function setup()
// FuzzyInput1
FuzzyInput *error = new FuzzyInput(1);
error->addFuzzySet(error_NB);
error->addFuzzySet(error_Z);
error->addFuzzySet(error_PS);
fuzzy->addFuzzyInput(error);
// FuzzyInput2
FuzzyInput *deltaError = new FuzzyInput(2);
deltaError->addFuzzySet(deltaError_NS);
deltaError->addFuzzySet(deltaError_Z);
deltaError->addFuzzySet(deltaError_PS);
fuzzy->addFuzzyInput(deltaError);
// FuzzyOutput
FuzzyOutput *speedOutput = new FuzzyOutput(1);
speedOutput->addFuzzySet(slowOutput);
speedOutput->addFuzzySet(normalOutput);
speedOutput->addFuzzySet(quickOutput);
fuzzy->addFuzzyOutput(speedOutput);
//---- Building FuzzyRule (1)-----------------------------
FuzzyRuleAntecedent *iferror_NBAnddeltaError_NS = new FuzzyRuleAntecedent();
iferror_NBAnddeltaError_NS->joinWithAND(error_NB, deltaError_NS);
FuzzyRuleConsequent *thenSpeedSlow = new FuzzyRuleConsequent();
thenSpeedSlow->addOutput(slowOutput);
FuzzyRule *fuzzyRule1 = new FuzzyRule(1,iferror_NBAnddeltaError_NS, thenSpeedSlow);
fuzzy->addFuzzyRule(fuzzyRule1);
//---- Building FuzzyRule (2)-----------------------------
FuzzyRuleAntecedent *iferror_ZAnddeltaError_Z = new FuzzyRuleAntecedent();
iferror_ZAnddeltaError_Z->joinWithAND(error_Z, deltaError_Z);
FuzzyRuleConsequent *thenSpeednormal = new FuzzyRuleConsequent();
thenSpeednormal->addOutput(normalOutput);
FuzzyRule *fuzzyRule2 = new FuzzyRule(2,iferror_ZAnddeltaError_Z, thenSpeednormal);
fuzzy->addFuzzyRule(fuzzyRule2);
//---- Building FuzzyRule (3)-----------------------------
FuzzyRuleAntecedent *iferror_PSAnddeltaError_PS = new FuzzyRuleAntecedent();
iferror_PSAnddeltaError_PS->joinWithAND(error_PS, deltaError_PS);
FuzzyRuleConsequent *thenSpeedquick = new FuzzyRuleConsequent();
thenSpeedquick->addOutput(quickOutput);
FuzzyRule *fuzzyRule3 = new FuzzyRule(3,iferror_PSAnddeltaError_PS, thenSpeedquick);
fuzzy->addFuzzyRule(fuzzyRule3);
// Add more rules to cover all combinations for better control
// ...
}
void loop()
{
int Readtemp1 = analogRead(A1); // Read temperature pin A1
int currentTemp = map(Readtemp1, 0, 1023, 0, 40); // Map temperature range (0-40°C)
Error = setpoint - currentTemp; // setpoint = 20
DeltaError = Error - previousError;
previousError = Error;
Serial.println(" ");
Serial.print(" Error = "); // Error
Serial.print(Error);
Serial.print(", DeltaError = "); // DeltaError
Serial.println(DeltaError);
fuzzy->setInput(1,Error);
fuzzy->setInput(2,DeltaError);
fuzzy->fuzzify();
Serial.print(" Error: error_NB-> ");
Serial.print(error_NB->getPertinence());
Serial.print(", error_Z-> ");
Serial.print(error_Z->getPertinence());
Serial.print(", error_PS-> ");
Serial.println(error_PS->getPertinence());
Serial.print(" DeltaError: deltaError_NS-> ");
Serial.print(deltaError_NS->getPertinence());
Serial.print(", deltaError_Z-> ");
Serial.print(deltaError_Z->getPertinence());
Serial.print(", deltaError_PS-> ");
Serial.println(deltaError_PS->getPertinence());
int output1 = fuzzy->defuzzify(1);
Serial.print(" Result: ");
Serial.print(output1);
PWMoutput += output1;
PWMoutput = constrain(PWMoutput, 0, 255); // Ensure PWM is within range
analogWrite(9,PWMoutput);
Serial.print(", PWMoutput : ");
Serial.println(PWMoutput);
delay(1000);
}
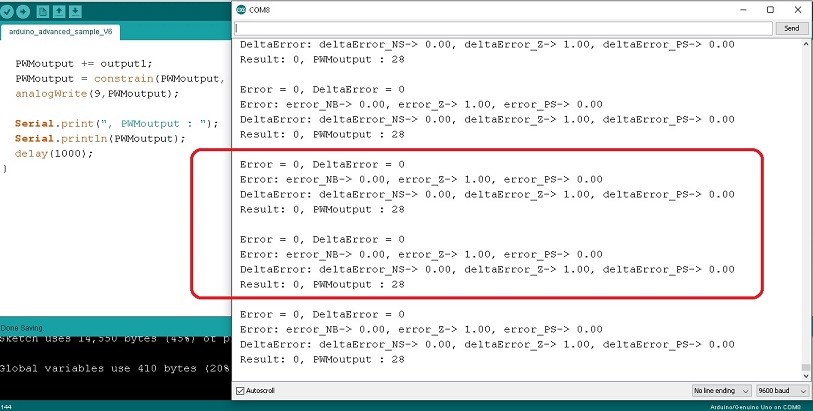
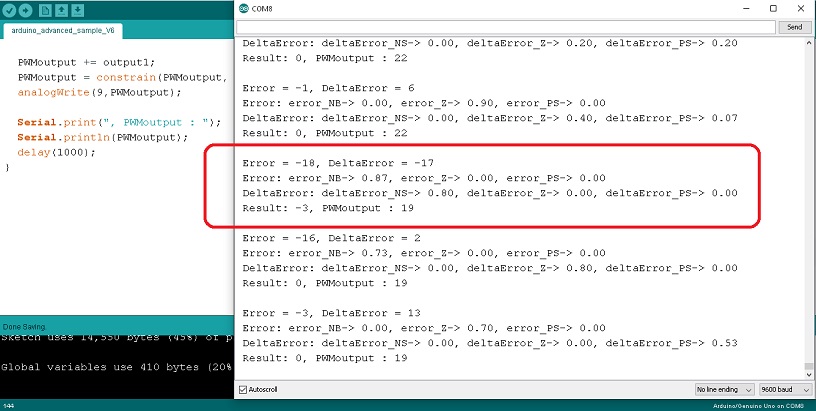
โปรแกรม Arduino สำหรับประมวลผลแบบฟัซซี่ลอจิกจะแบ่งออกเป็น 3 ส่วนคือ ในส่วนแรกที่คำสั่ง #include <Fuzzy.h> จะทำหน้าที่ประกาศใช้งานฟังก์ชั่นไลบารี่ฟัซซี่ลอจิก ถัดลงมาจะเป็นการกำหนดค่า FuzzyINPUT, FuzzyOUTPUT (ซึ่งจะต่างกับ EP4 เล็กน้อย) ส่วนที่สอง void setup() ที่หน้าที่กำหนดอัตราการสื่อสารของพอร์ตอนุกรมเท่ากับ 9600, FuzzyRule และการกำหนดความกว้างของสัญญาณพัลซ์วิดธ์มอดูเลตชั่นที่ขา D9 ด้วยคำสั่ง analogWrite(9,output); ส่วนที่สาม void loop() จะทำหน้าที่รับค่าสัญญาณอินพุตด้วยคำสั่ง int Readtemp1 = analogRead(A1); จากนั้นจะใช้คำสั่ง int input = map(Readtemp, 0, 1023, 0, 40); เพื่อเปลี่ยนค่าที่อ่านได้ 0-1023 ให้อยู่ในช่วง 0-40 (หมายถึงช่วงอุณหภูมิ 0-40°C) และแสดงผลด้วยคำสั่ง Serial.print(input); จากนั้นจะเป็นคำสั่ง Error = setpoint – currentTemp; DeltaError = Error – previousError; previousError = Error; เพื่อให้ได้ค่า Error และ DeltaError สำหรับอินพุต fuzzy->setInput(1,Error); fuzzy->setInput(2,DeltaError); ในการประมวลผล ด้วยคำสั่ง fuzzy->fuzzify(); และให้แสดงผลที่เกิดขึ้นด้วยคำสั่ง Serial.print(Error:); , Serial.print(deltaError:); ต่อมาที่คำสั่ง int output1 = fuzzy->defuzzify(1); ซึ่งจะได้ค่าเอาต์พุตออกมาที่ตัวแปร output1 เพื่อกำหนดสัญญาณพัลซ์วิดธ์มอดูเลตชั่นที่ขา D9 ด้วยคำสั่ง PWMoutput += output1; PWMoutput = constrain(PWMoutput, 0, 255); และ analogWrite(9,PWMoutput); ตามลำดับ
ในการทดลองนี้จะกำหนด FuzzyRule ไว้เพียง 3 ส่วนคือ

สำหรับการกำหนดกฏของฟัซซี่ลอจิกที่ตำแหน่ง Building FuzzyRule1, 2 และ 3 ในตัวอย่างนี้ ผู้ออกแบบระบบควบคุมจะต้องทดลองปรับให้ระบบการทำงานเป็นไปตามที่ต้องการ (เช่นเดียวกับ EP4) โดยสามารถปรับตัวเลขภายในหรือเพิ่มจำนวน FuzzyINPUT, FuzzyOUTPUT และกฏของฟัซซี่ลอจิก FuzzyRule ให้เหมาะสมกับระบบที่ต้องการควบคุมนั้นๆ ได้
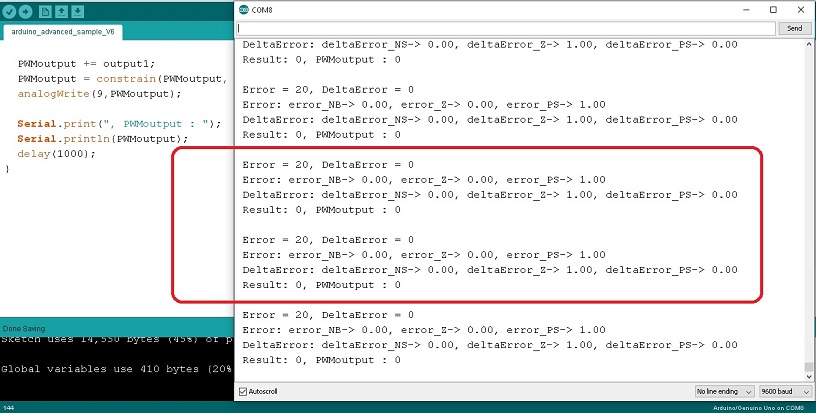
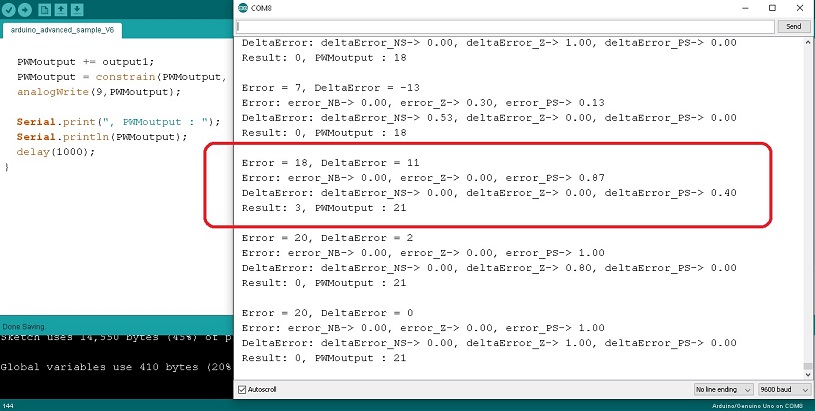
สำหรับในตอนสุดท้ายของการควบคุมอุณหภูมิแบบฟัซซี่ลอจิก (Fuzzy Logic Control : FLC) โดยใช้บอร์ด Arduino UNO ครั้งนี้ จะเป็นอีกตัวอย่างหนึ่งของการควบคุมอุณหภูมิด้วยการกำหนดค่า Setpoint ซึ่งจะคล้ายกับการควบคุมแบบ PID Control ดังนั้นการเลือกเขียนโปรแกรมฟัซซี่ลอจิกสำหรับนำไปควบคุมการทำงานในระบบ จะขึ้นอยู่กับผู้ออกแบบและการปรับจูนในโปรแกรมให้ระบบทำงานได้อย่างเหมาะสม
Reference
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fuzzy_control_system
- https://forum.arduino.cc/t/how-make-fuzzy-logic-coding-for-arduino-uno/282381/4
- https://github.com/alvesoaj/eFLL
- https://github.com/amimaro/FuzzyLibrary
- https://fuzzylite.com/
- https://fuzzylite.com/downloads/FuzzyLite-Libraries.pdf
- https://www.microjpm.com/products/ad52300/
- https://c1555f5ec9.clvaw-cdnwnd.com/34662fcf1f1e607c561442431023ac8e/200010020-73ac173ac3/AD52300%20uJPM%20Datasheet.PDF
- https://www.tinkercad.com/dashboard
- https://www.circuitbasics.com/arduino-thermistor-temperature-sensor-tutorial/
- https://gemini.google.com/
- https://copilot.microsoft.com